Regulation of Repair Response Genes:
An ADP-ribose moiety, derived from the cleavage of ribose nicotinamide glycosidic bond of NAD, by an unknown mechanism, spontaneously leads to the polymerization of ADP-ribose into poly ADP-ribose.� Interestingly and importantly, DNA strand breakage also leads to such poly ADP-ribose formation.
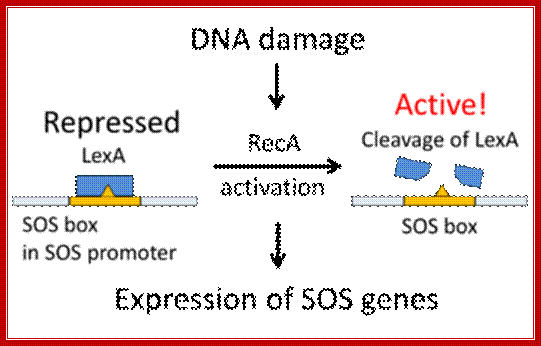
When DNA is severely damaged, cells respond in synthesizing required proteins to repair immediately; http://2012.igem.org/
�
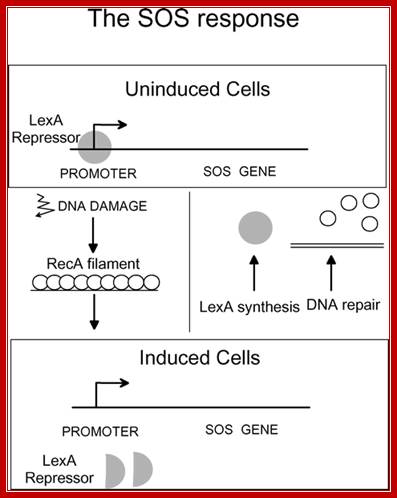
When DNA is significantly damaged (e.g., by exposure to UV radiation or chemicals), several DNA damage-related proteins are synthesized quickly. This reaction to DNA damage is known as SOS response. Http://2012.igem.org/
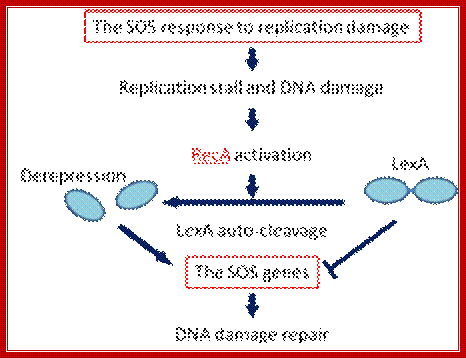
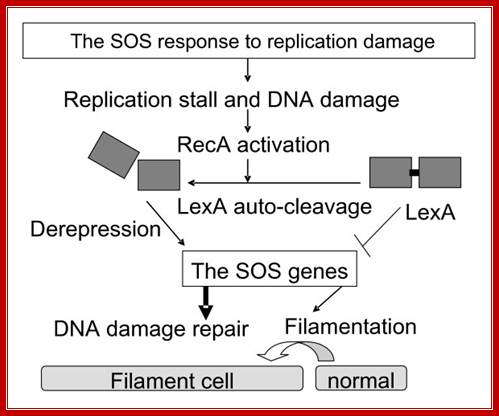
Top Fig; If DNA is significantly damaged (eg by exposure to UV radiation or chemicals), synthesis of several DNA damage-related proteins occurs quickly. This reaction to DNA damage is the SOS response. Osaka Project; http://2011.igem.org/
Bottom Fig; The SOS response. LexA and RecA control the SOS genes that encode functions required for DNA damage repair. LexA represses these genes. DNA damage activates RecA to stimulate autocatalytic cleavage of LexA so that the SOS genes are derepressed and expressed for repair. Cell division is inhibited and delayed resulting filamentation to allow repair before cell division.
The SOS response LexA and RecA control SOS gene that encode functions required for DNA damage repair. Dallo and Weitao; http://www.infectagentscancer.com/
Damages to DNA sends signals in the form of small molecules to certain regulons involved in DNA-damage repair processes, so as to halt further damage and salvage the DNA from further damage, whatever the kind of damage has happened.
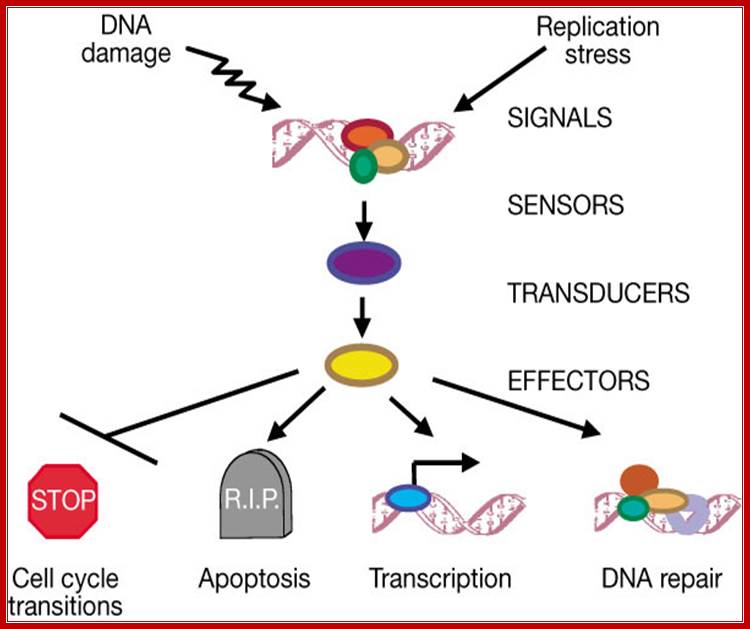
A contemporary view of the general outline of the DNA damage response signal-transduction pathway.;
Bin-Bing S. Zhou & Stephen Elledge. J; http://www.nature.com/
The genes for repair are clustered and modulated or regulated as four
operons.
1. SOS groups; (e.g. Uvr.A, B and C; Rec-A, Umu-C and Umu-D).
2. Ada gene group: (methyl transferases, N-glycosylases).
3. Sox-R (endonucleases IV).
4. Kat-F (exonuclease-III, catalase III).
In addition to the above there are many more regulons (many operons regulated by a common factor) that respond to oxidative stress, which can generates oxygen free radicals, which can cause DNA damage.� Heat-shock can also activate such SOS systems.� UV radiations, alkylating agents and cross linking of DNA strands can induce SOS response.
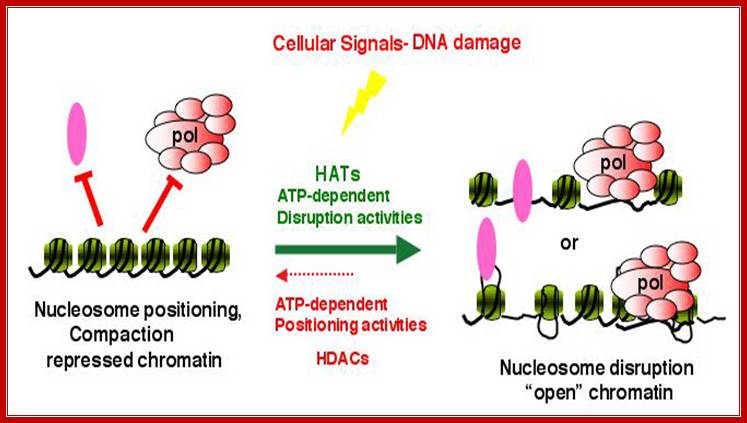
This figure illustrates how eukaryotic systems send signal if the cellular DNA is damaged to activate certain genes required for the repair.� One of the activating complex is HATs which disrupt inactive nucleosomal compacted chromatin into open structure for accession of RNA pol complexes.� Disruption is due to Acetylation of Histone tails; http://www.microb.uni.wroc.pl/
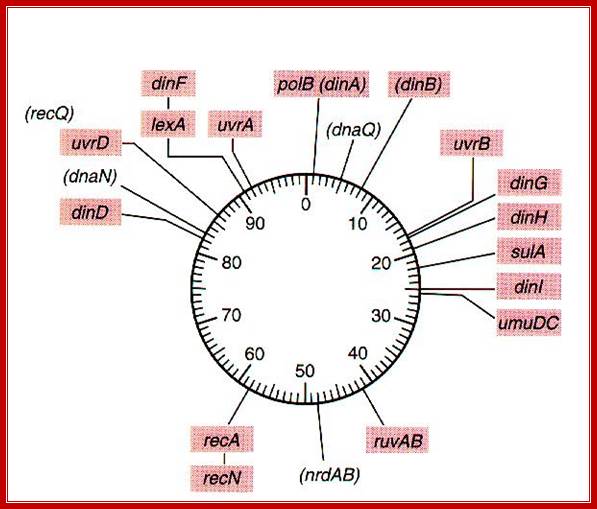
SOS regulated genes in bacteria; http://cmgm.stanford.edu/
� Damages in the form of methylations to Guanines or alkylating agents activate excision repair system.����
� Other forms of damages do activate other repair gene clusters including recombination repair system.�
� In eukaryotic systems DNA damage inhibits cell cycle to enter into mitotic phase until the DNA damage is repaired and DNA replication is not completed and the cell cycle does not enter into G2 stage or M-stage.
� In SOS system of regulation, broken ssDNA and other forms of damages to DNA activate Rec-A, where Rec-A gets self-activated.
� Rec-A mediated repair system requires ss broken DNA strands and ATP at the sites of damage.
� The activated Rec-A (ss-broken DNA activates Rec-A), which also endowed with protease activity interacts with Lex-A proteins and activates their latent protease activity.
� Lex-A proteins are repressors for a group of genes that respond to molecular SOS (Save Our Souls) signals.�
� Lex-A proteins, of 22kd molecular mass, possess a latent protease domain.��
� Activated Lex-A proteins, because of its inherent protease activity, perform autocatalytic activity (the peptide bond between ala-gly are cleaved).�
� This leads to conformational changes in the Lex-A protein, which renders the protein to dissociate from the operator region of each of the genes involved in SOS response gene clusters, thus relieve repression of all said genes.�
� Rec-A also causes lytic expression of lysogenic lambda phage due to cleaving of repressor proteins.
� The SOS gene clusters contain, which are repressed by Lex-A proteins- Rec-A, Lex-A, Uvr-A, UVR-B, Umu-C and Umu-D.
� Umu-D, activated by RecA, by self-cleavage functions in mutagenic bypass.
� In this process, the activated Umu-D protein with Umu-C and rec-A and DNA pol-III, as a complex called mutasome, assemble at lesion site and make the polymerase to bypass the lesions.
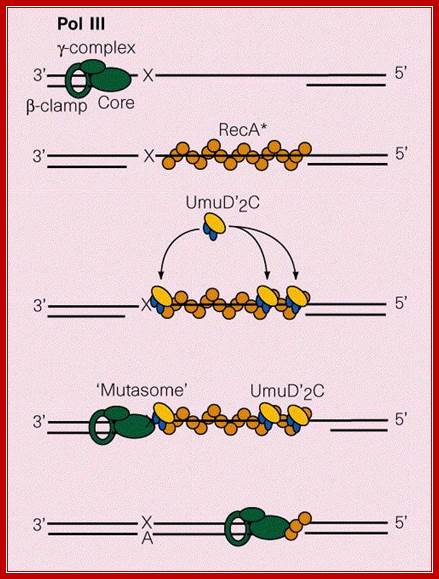
Genes activated by SOS response, some as shown above, organize on a damaged or broken strand into mutasomes that repair damaged DNA strands; however the repair is error prone, not perfect. http://cmgm.stanford.edu/
� him-A, also called �din� genes (damage inducible) is another gene that is involved in DNA repair system.�
� The repressor, Lex-A binds to the promoter region of each of the above-mentioned genes to a sequence box called SOS box.�
� This operator region consists of 20 base pairs block, which contains the sequence 5�CTG N10 CAG 3�.� This sequence also overlaps the promoter region.�
� There are at least 43 genes respond to SOS signals.
� The SOS response makes the Lex-A protein to dissociate from each of the promoters�� and each of the genes are transcribed or can be called as activated.�
� As Rec-A is induced; it activates its own gene to produce more of Rec-A products.
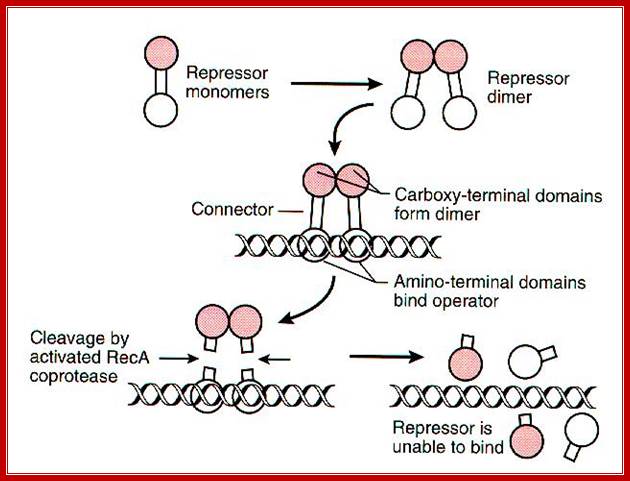
Lex-A repressor, activated by RecA, undergoes autocatalysis and the peptide bond between between Alanine and Glycine is cleaved.� This makes the repressor inactive and it now frees from the promoter elements of respective genes; thus, the said genes get activated, and they are involved in the repair of damaged DNA. http://cmgm.stanford.edu/
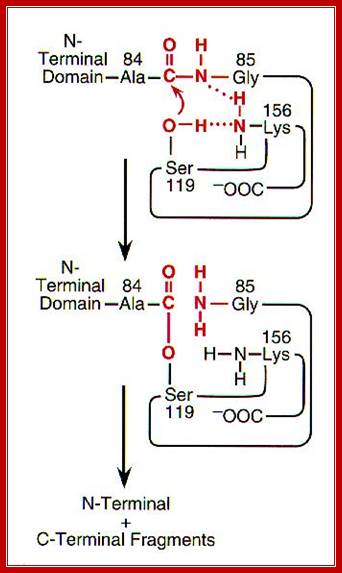
Activated RecA induces Lex A for auto proteolysis, thus LexA becomes inactive and drops down from operator regions of respective operons and genes. http://cmgm.stanford.edu/
� Activated Rec-A inactivates all Lex-A proteins so as to allow all the SOS response genes to continuously transcribe and produce the products for DNA repair. Activated Rec-A interacts with Lex-A proteins and activates Lex-A�s hidden protease activity; this protease activity leads to self-cleaving.� When the Lex-A proteins are self-cleaved, they undergo conformational changes and dissociate from the operators and allow each of the genes to be transcribed.
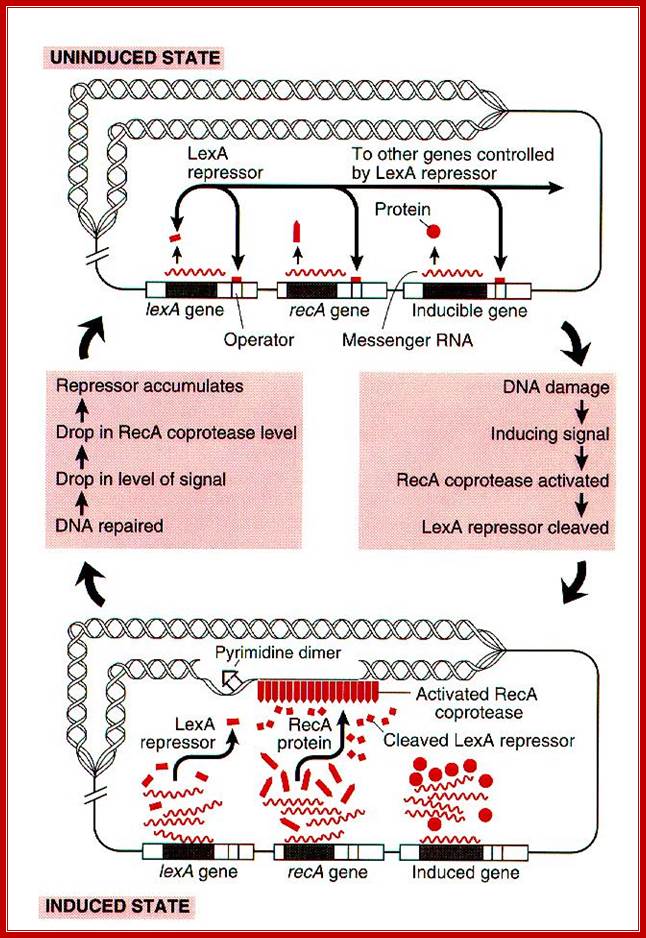
SOS gene regulation; http://cmgm.stanford.edu/
� When all DNA damage is repaired, and no damaged DNA strands are available, Rec-A becomes inactive, and so Lex-A become active.
� They bind to each of their promoters and block transcription of SOS response gene clusters.
� UVR-A, Uvr-B, UVR-C, together perform excision repair process.
� Uvr-C and Uvr-D together encode protein for error prone repair process.
� Uvr-D is a helicase-II.
� Umu-C and Umu-D together perform mutagenic bypass.
� Sfi-A and Sfi-B together inhibit cell division if the cellular DNA is damaged or not fully replicated.
� Rec-A, Q, N, UVR-D, him-A, ruv, are involved in recombination repair.
� Him-A- is a subunit of integration factor involved in site-specific recombination.
� Rec-N is involved recombination repair process.
� Din-A, din-B, dinD and din-I; Din means Damage inducible gene(s).