Genetic RNA:
Introduction:
Those RNAs that have the ability to replicate, mutate, undergo recombination and perform protein synthesis using its encoded information; virtually behaving like a DNA are called Genetic RNAs.� Most of the genetic RNAs are found in viruses, viroids and virusoids.
A list of few RNA Viruses, Viroids and Virusoids:
|
Virus |
Shape |
Nature |
Size and number of genome |
Single stranded; +/- sense |
|
TMV (Tobacco mosaic virus) |
Rod |
Naked |
RNA-Single, 6395 ntds |
Single stranded, (+) sense |
|
RSV (Rous sarcoma Virus) |
Isometric |
Enveloped |
RNA-2n, 8000 ntds |
Single stranded, (+) sense |
|
Picorna virus |
Isometric |
Naked |
RNA-Single, 7433 ntds |
Single stranded, (+) sense |
|
Rhabdo virus |
Bullet |
Enveloped |
RNA-Single, 11,000 ntds |
Single stranded, (-) sense |
|
Influenza virus |
Spherical |
Enveloped |
RNA-Eight, size vary |
All single stranded, (-) sense |
|
Reo Virus
|
Isometric |
Naked |
RNA-Ten, size vary |
All double stranded, (+/_) sense |
|
MS2, Qbeta, phages |
Isometric |
Naked |
RNA-4400 ntds, One, |
Single stranded, (+) sense |
|
HTLV-I and II |
Isometric |
Enveloped |
RNA-Two, ~8.2 Kb each |
Single stranded, (+) sense |
|
HIV-I and II |
Isometric |
Enveloped |
RNATwo, ~8 �to 9 kb |
Single stranded, (+) sense |
|
Viroids |
PSTV |
|
RNA-circular |
Prions-proteins |
|
Virusoids |
Tobacco ringspot virusoid |
|
RNA |
|
General Features:
- The genomic RNAs that are found in bacterial viruses, plant viruses and some animal viruses are called Genetic RNAs. They have structural and functional features encoding information in the form of polynucleotide chain of specific length, and sequence for certain polypeptides.�
- The Genetic RNAs are stable. Theirs inherent features like, capable of undergoing mutations, recombination, and replication and perform function as cistrons (production of polypeptide chains) are the fundamental properties of life.
- Genetic RNAs replicate to generate a number of copies and functions in producing specific polypeptides chains, which exhibits inheritance features.
- The genomic RNAs are mostly single stranded, but double stranded RNAs are not uncommon. The single stranded RNAs are encoded with positive sense (it can be directly used for translation) or negative sense (this cannot be used for translation), but it can be used for replication only to produce (+) ve chain.�
- One finds double stranded RNAs as genetic materials.�
- The number of copies per virus can very from one (in most of the cases) to two of the same type (HIV-I and II).� In some there can be 8 to 10 genomic RNA segments, each having different genetic information, bundled together ex. Influenza virus.�
- In few cases 10 different double stranded RNA segments are found, ex. Reovirus.
- Whether they are single stranded or double stranded, monopartite or multi partite genomes, with plus or minus sense, undergo replication, recombination or mutation in host cells.
- They carry coded information for at least two to three polypeptides, among them major components are capsid proteins.� They always produce their own RNA Replicase enzymes.
- In extreme cases, the genomic RNAs exists either in linear form or circular form and naked without any association with proteins ex. Viroidal RNAs.�
- Another category of RNAs which have no independent existence of their own, but live with other genomic materials as associates and require assistance from them for their replication, such RNAs are called satellite RNAs.
Those RNAs, that have the ability to replicate, mutate, undergo recombination and perform protein synthesis using its encoded information; virtually behaving like a DNA, are called Genetic RNAs.� Most of the genetic RNAs are found in viruses, viroids and virusoids. No such RNAs are observed or detected in plants or animals
RNAs, those, endowed with all potentialities to replicate, mutate, recombine and perform function, are called genetic RNAs, for they act and behave like any DNAs that act as genetic materials.� Almost all genetic RNA are found in few classes of viruses and viroid�s and virusoids.
Viroids: Thy are little larger than Proteinaceous Prions. Viroids contain short RNA without proteins.� The size of Viroidal RNA is about 250-450 nucleotides.� Viroids, were the first discovered in 1971, as pantheons� Theodor Otto Diener, plant pathologist at the U.S Department of Agriculture's Research Center in Beltsville, Maryland. The first viroid discovered was Potato spindle tuber viroid (PSTV), there are 33 species of PSTV. They don�t code for any proteins replicate using host RNA polymerase II, which canalizes rolling circle model for synthesis using viroidal RNA.� Some viroidal RNAs act as ribozymes which cleave and self-ligates.� Viroids are considered as relics of ancient RNA world.
Theodor Otto Diener, plant pathologist at the U.S Department of Agriculture's Research Center in Beltsville, Maryland, found that most of the viroids replicate in the nucleus or in chloroplasts.� Using host RNA PoI catalyzes rolling circle production using viroidal RNA
![]()
httrp://www.wikimedia.org; PSTV viroid.
Virusoids: They are single stranded, circular RNAs; they are dependent on plant viruses for their replication and their viral coating. The size of RNA can be several hundred nucleotides long.� They replicate by rolling circle mode.� Virusoids are often called Satellite nucleic acids, now they are called satellites.
Prions: They are infectious agents composed of proteins only called Prps.� They are infectious agents. Their proteins can fold into different forms; some of them cause bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE)�called mad-cow disease. Human prion diseases include Creutzfeldt�Jakob disease (vCJD) and its variant Gerstman�Str�ussler�Scheinker syndrome, fatal familial insomnia, and kuru.� Prions on infection causes human proteins to fold into misfolded prion form.� Prions are found in plants as well as animals including humans.
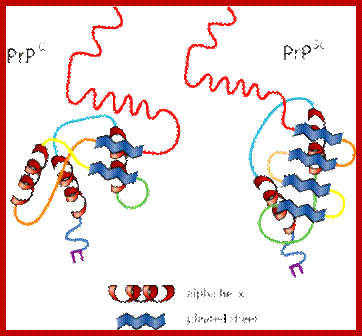
Prion: http://virology-microbiology-b.blogspot.in/
Prions;https://en.wikipedia.org